Dbs101_flippedclass6
Document based databases.
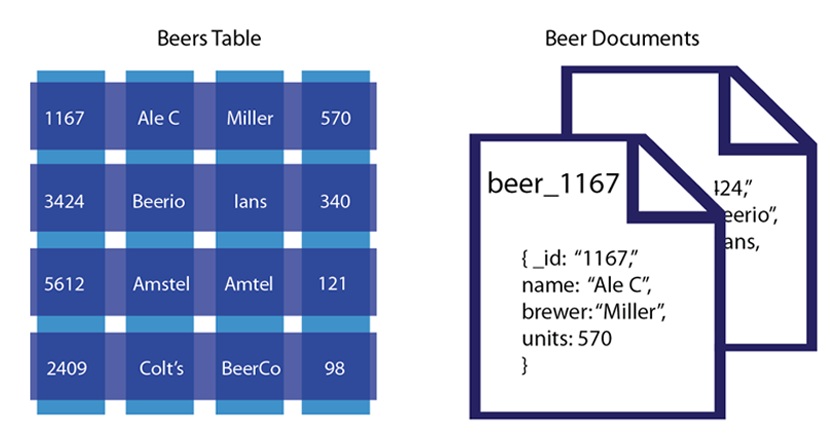
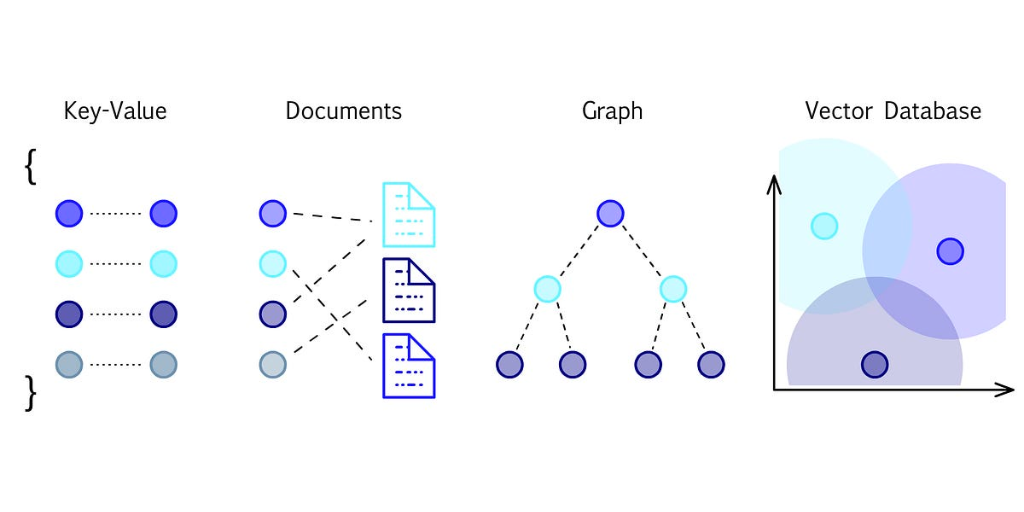
Document based database is a type of NoSQl database which does not use the relational model to store data, instead it uses the documents to store the data in the database.
A document database stores data in JSON, BSON, or XML documents.
Documents can be stored and retrieved in a form that is much more similar to a dictionary with keys and value.
Elements can be accessed by using the index value that is assigned for faster querying
Differences between the relational database model and document based database.
| Relational Database Model | Document database |
|---|---|
| 1. Data are stored using rows and columns in a table | 1. Data is stored using documents . |
| 2. Uses SQL commands | 2. Uses NOSQL commands. |
| 3. Relational databases have a structured schema that defines the tables, columns, data types, constraints, and relationships between tables. | 3. Document databases have a flexible schema, allowing documents within a collection to have varying structures. |
| 4. There are relationships between the tables and it is referred using FOREIGNl KEYS. | 4. There is no dynamic relationship between two documents so documents can be independent of one another. |
Key-Value based databases.
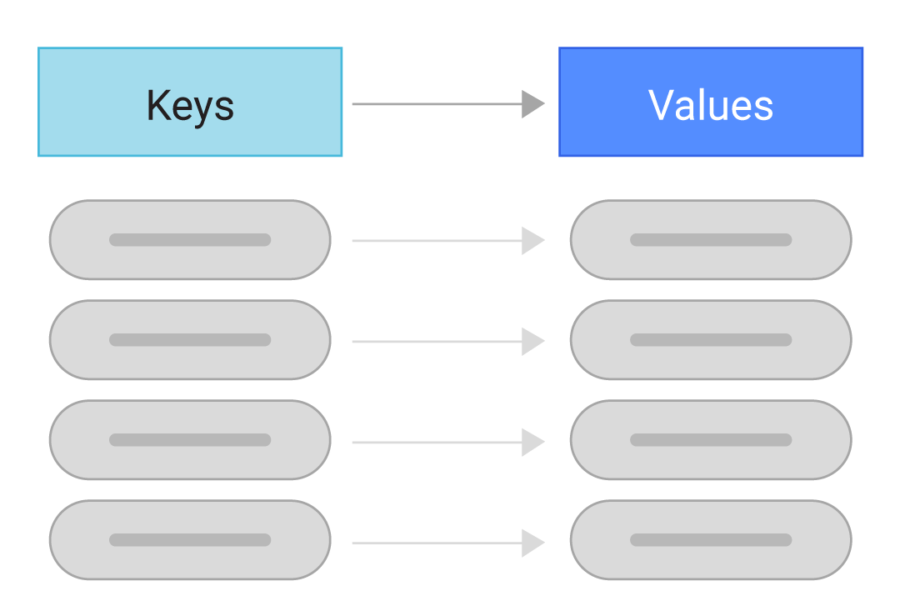
Key value database is another type of database that does not use tables to store data; instead, every data element in the database is stored in key-value pairs.
Data is retrieved using the unique key allotted to each element in the database.
Key value databases only have two columns, one for key and one for their value.
The value stored can be simple data types like strings and numbers or complex objects.
Features on the key value db
Simplicity
Key-value databases have one of the simplest data models among NoSQL databases.
schemas are less fashioned there for data is stored in key value format in two columns.
Scalability
support data replication which means maintaining multiple copies of data across different nodes, allowing the system to continue operating even if some nodes fail.
Horizontal scalability, also known as scaling out, refers to the ability to increase the capacity or performance of a system by adding more hardware or resources.
Horizontal scalability involves adding more servers or nodes to handle increased workload or data volume.
Speed
- Since data is accessed directly by its unique key, retrieval times are typically fast and predictable, especially for simple lookup operations
Graph Database
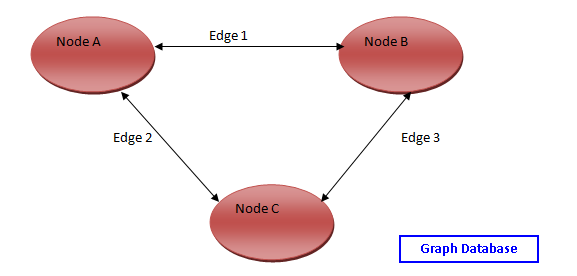
A graph database is a type of database management system (DBMS) specifically designed to store and manage data whose relationships are represented in a graph structure.
In a graph database, data entities are depicted as nodes, and the relationships between these entities are illustrated as edges or connections between the nodes.
Nodes : Nodes are vertices that store the data objects. Each node can have an unlimited number and types of relationships.
Edges : Edges represent relationships between nodes. For example, edges can describe parent-child relationships, actions, or ownership. They can represent both one-to-many and many-to-many relationships. An edge always has a start node, end node, type, and direction.
Properties : Each node has properties or attributes that describe it. In some cases, edges have properties as well. Graphs with properties are also called property graphs.
Graph databases are utilized in various industries and applications where data relationships are complex and interconnected.
Use Cases of Graph Database :
- Generative AI
- Telecommunications
- Healthcare and Life Science
Vector Databases
A vector database is designed to store, manage, and index massive quantities of high-dimensional vector data efficiently. What is high-dimensional vector data?
High-dimensional vector data refers to data that is represented as vectors in a space with a large number of dimensions. Each dimension in the vector corresponds to a different attribute, feature, or variable.
Example : In image processing, high-dimensional vectors can represent images as vectors of pixel values, with each dimension corresponding to a pixel in the image.
In natural language processing (NLP), high-dimensional vectors can represent words or documents in a vector space model where each dimension corresponds to a different word or term in the vocabulary.
In a vector database, data can be identified based on similarity metrics instead of exact matches, making it possible for a computer model to understand data contextually.
How do vector databases work ?
Vectors in a vector database typically refer to high-dimensional numerical representations of data entities. These vectors can represent various types of data, such as text, images, audio, or any other form of structured or unstructured information.
Each vector in a vector database corresponds to an object or item, whether that is a word, an image, a video, a movie, a document, or any other piece of data.
These vectors are likely to be lengthy and complex, expressing the location of each object along dozens or even hundreds of dimensions.
Vector databases are used for :
- Finding similarity and semantic searches
- Machine learning and deep learning
- Large language models (LLMs) and generative AI like ChatGPT
Time-series Databases
A time series database (TSDB) is a specialized type of database that is specifically designed to efficiently store, retrieve, and analyze time-stamped or time series data.
Time series data is simply measurements or events that are tracked, monitored, downsampled, and aggregated over time.
Each data point in a time series database is tagged with a timestamp indicating when the data was recorded or observed.
Time series databases were primarily focused on looking at financial data, the volatility of stock trading, and systems built to solve trading.
When is the time series database used ?
When an application needs data that accumulates quickly and your other databases are not designed to handle that scale.
When your application needs to perform real-time analysis of billions of records.
When an application needs to perform online queries at millisecond timescales and support CPU-efficient ad-hoc queries.
Column oriented Databases
A columnar database, or column-oriented database, is a type of database management system (DBMS) that organizes and stores data in a column-wise manner, as opposed to traditional row-wise storage used in relational databases.
This enables faster queries for data analytics, which generally involves filtering and aggregating table columns.
When data is stored in a columnar database, it enables faster queries for data analytics, particularly those involving filtering and aggregating table columns, due to several key advantages like
Faster Access : data is stored column by column, the database only needs to look at the columns needed for a query. This means it doesn’t waste time scanning through entire rows, which speeds up the process.
Aggregation Optimization : These databases are good at doing operations that involve adding up or summarizing data across columns, like finding averages or totals. Since each column is stored separately, these operations can focus on just the relevant data, speeding up the process.
Parallel Processing : Columnar databases can spread out the work across multiple processors or computers, which helps handle large amounts of data quickly.
| Situation | Benefits of Columnar Databases | |
|---|---|---|
| Data Filtering | - Faster access: Only necessary columns are accessed. | |
| - Efficient processing: Queries focus on relevant data. | ||
| - Compression: Data is stored efficiently, saving space. | ||
| Data Aggregation | - Group operations: Ideal for summarizing data. | |
| - Speed: Aggregations are faster due to column storage. | ||
| - Parallel processing: Can handle large datasets easily. | ||
| Overall | - Improved performance for analytics and data insights. | |
| - Scalability: Suitable for handling large amounts of data. |
- Columnar databases are great for data analytics. They scan fewer rows and process less data than row-oriented databases.
When to use columnar database ?
You should use columnar databases when you intend to filter and aggregate data logically stored in columns.
The amount of stored data greatly affects the performance contrast between columnar and row-oriented databases. Columnar databases, organizing data by column, offer better storage efficiency and compression, particularly advantageous for large datasets.
They excel in analytical queries, aggregations, and scalability, leveraging parallel processing. This amplifies their performance advantage as data volumes increase, accentuating their efficiency, speed, and scalability for analytical tasks compared to row-oriented databases.
| Use Columnar Databases When… | Use Row-Oriented Databases When… |
|---|---|
| Your primary use case is analytics | Your primary use case is transactions |
| You need low query latency | You don’t need low query latency (for analytics) |
| You have large amounts of data | You’re working with smaller data (for analytics) |
| You don’t need strict ACID compliance | You need strict ACID compliance |
| You’re using event sourcing principles | You need to do frequent, small replaces and deletes |
| You need to store and analyze lots of time series data | You need to store and access records with unique IDs |