Dbs101_flippedclass9
Query Optimization
What is query optimization?
Query Optimization is a crucial aspect of database management systems (DBMS) that seeks to determine the most efficient way to execute a given query by considering a variety of query execution strategies. The goal is to minimize the system resources required to fulfill the query and increase the speed of returned results.
At its core, Query Optimization involves the evaluation of different query plans and choosing the one with the least estimated cost.
Key features of Query Optimization include:
Parsing : Translates SQL queries into a query tree.
Transformation : Optimizes the query tree through simplification, normalization, and optimization.
Cost Estimation : Evaluates the cost of each potential execution plan.
Plan Selection : The DBMS selects and executes the most cost-effective plan.
Query Plan ?
A query plan, also known as an execution plan, is a detailed strategy that a database management system (DBMS) creates to execute a query. It outlines the steps and operations the DBMS will take to retrieve the desired data from the database efficiently.
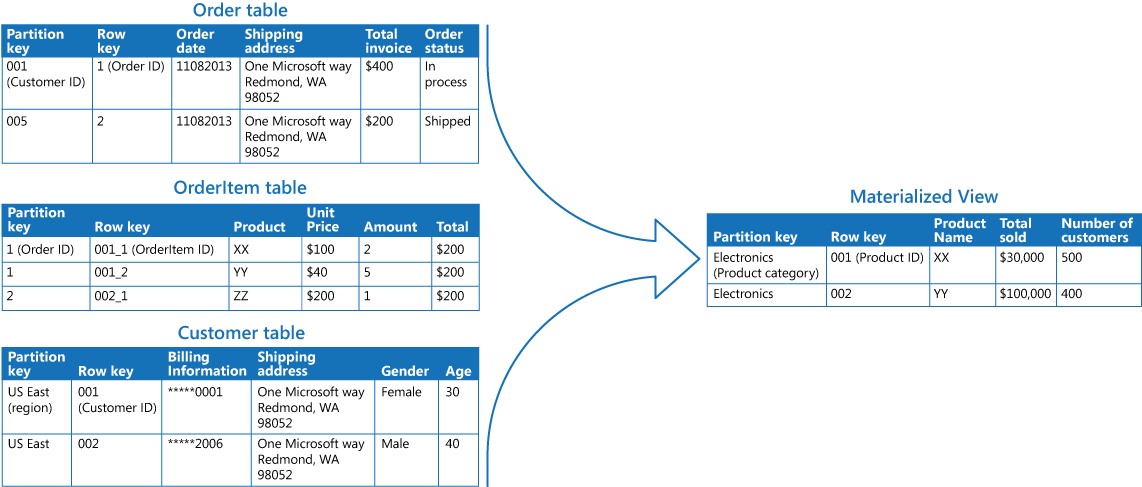
MaterialisedViews
A materialized view is a duplicate data table created by combining data from multiple existing tables for faster data retrieval.
Advanced Query Optimization in DBMS
Query Optimization is a technique of analyzing and deciding an execution plan that computes the result of the query using less number of resources.
The main goal of query optimization is to find an execution plan for that query to reduce the time required to process it.
Two main objectives of Query Optimization are:
- Determine the optimal plan to access the database.
- Reduce the time required to execute the query.
Components of query optimization
There are three components of optimizer :
- Transformer
- Estimator
- Plan Generator
Transformer
A Query Transformer is a part of the query optimization process in a database management system (DBMS) that takes a parsed query and attempts to rewrite it in a way that potentially reduces the cost of executing the query.
The parsed query is typically represented as a set of query blocks, which are logical units of the query, such as SELECT statements, subqueries, and clauses (e.g., WHERE, GROUP BY).
Estimator
It determines the over all cost of execution plan. This estimator uses three different measures to determine cost which includes:
Selectivity: It is defined as a fraction of rows from a row set. Cardinality: It is defined as the number of rows returned by each operation in executed plans. Cost: IT defines the estimated resource consumption for a plan.
To estimate cost, optimizer uses following factors:
- System resources (CPU, Memory and I/O)
- Cardinality
- Size of initial data set
Plan Generator
It explores various plans for query block by checking various access paths, join methods and join orders. After checking various paths, optimizer picks the path with the lowest cost.
Methods Of Query Optimization in DBMS
There are two methods of Query Optimization in DBMS:
- Cost Based Query Optimization in DBMS
- Adaptive Query Optimization
Cost Based Query Optimization in DBMS
Cost-Based Query Optimization (CBO) is a sophisticated and systematic approach used by database management systems (DBMS) to determine the most efficient way to execute a query.
1. What is Cost-Based Query Optimization?
Cost-Based Query Optimization is a method where the optimizer assigns a numerical value, known as cost, to each step in the execution plans of a given query.
The optimizer evaluates all possible execution plans and selects the one with the lowest estimated cost.
2. Adaptive Query Optimization in DBMS
Adaptive Query Optimization (AQO) is a dynamic approach in database management systems (DBMS) where the optimizer can make changes to execution plans during query execution.
This flexibility allows the optimizer to respond to new information that becomes available as the query runs, leading to more efficient query execution, especially when initial statistics are insufficient or outdated.